The APPSC Group 2 Mains consists of two papers. Each paper carries 150 marks. A total of 300 marks. Each paper will have 150 minutes.
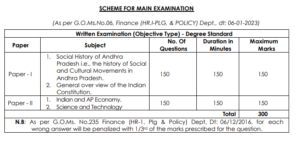
APPSC Group-II Mains Paper I Syllabus :
Section-A: Social and Cultural History of Andhra Pradesh-75 marks :
Pre-historical cultures – Satavahanas, Ikshvakus: socio-economic, religious conditions, literature, arts, architecture – Vishnukundins, Vengi Eastern Chalukyas, Andhra Cholas: Society, religion, Telugu language, architecture, sculpture.
The various major and minor dynasties that ruled Andhra between the 11th and 16th centuries – socio-religious and economic conditions, and the development of Telugu language, literature, art and architecture in Andhra Pradesh between the 11th and 16th centuries.
Arrival of Europeans – Trade Centers – Andhra under the company – 1857 revolt, its impact on Andhra – Establishment of British rule – Socio-cultural awakening, Justice Party/ Self-respect movement – Growth of Nationalist Movement in Andhra between 1885 and 1947 – Socialists – Role of Communists – Anti-Zamindari and Kisan movements– rise of nationalist poetry, revolutionary literature, plays, women’s participation.
The birth and rise of the Andhra movement – the role of the Andhra Mahasabhas – prominent leaders – the events that led to the formation of andhra state 1953 – the role of the press and newspapers in the Andhra movement – the role of the library movement, folk and tribal culture.
The events leading up to the formation of the state of Andhra Pradesh – The Vishalandhra Mahasabha – the States Reorganisation Commission, its recommendations – the Gentlemen’s Agreement – important social and cultural events from 1956 to 2014.
Section-B: Constitution of India-75 marks :
Nature of The Constitution of India – Constitutional Development – Salient Features, Indian Constitution – Preamble – Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, their relationship – Fundamental Duties – Constitutional Amendment – Fundamental Structure of the Constitution.
Structure and functions of the Government of India – Legislative, Executive and Judiciary – Types of Legislatures: Unicameral, Bicameral – Executive – Parliamentary – Judiciary – Judicial Review – Judicial Activism.
the distribution of legislative and executive powers between the Centre and the States; Legislative, administrative and economic relations between the Centre and the States- Powers and duties of constitutional institutions – Human Rights Commission – RTI – Lokpal, Lokyukta, Centre-State relations – Need for reforms – Rajmannar Committee, Sarkaria Commission, M.M. Poonchi Commission – Unified, federal characteristics of Indians Constitution – Indian political parties – Party system in India – Recognition of national and state parties – Elections, electoral reforms – Anti-defection law.
Centralization Vs Decentralization – Social Development Program – Balwant Rai Mehta and Ashok Mehta Committees – 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts and their implementation.
APPSC Group-II Mains Paper II Syllabus :
Section-A: Indian, Andhra Pradesh Economy-75 marks :
Structure of the Indian Economy, Economic Planning, Policies: India’s National Income: Concept and Measurement of National Income – Professional Model of Income in India and Distribution of Sectors – Economic Growth and Economic Development – Planning Strategy in India – New Economic Reforms 1991 – Decentralization of Financial Resources – NITI Aayog.
Monetary, Banking, Public Finance, Foreign Trade: Functions and Measures of Money Supply – Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Functions, Monetary Policy, Debt Control – Indian Banking: Structure, Development and Reforms – Inflation: Causes, Remedies – India’s Economic Policy: Financial Imbalance, Fiscal Deficit, Fiscal Liability – Indian Tax Structure – Goods and Services Tax (GST) – Recent Budget of India – India’s Balance of Payments (FDI) – FDI.
Agriculture Sector, Industrial Sector, Services in The Indian Economy: Indian Agriculture: Cropping Policy, Agricultural Production and Productivity in India : Agricultural Finance and Marketing in India : Issues and Actions – Agricultural Prices and Policy in India: MSP, Procurement, Issuing Price and Distribution – Industrial Development in India: Models and Problems – New Industrial Policy, 1991 – Disinvestment – Ease of Doing Business – Industries Collapsing: Causes, Consequences and Mitigation Measures in India: Growth and cooperation of the services sector in India – developing the role of IT and ITES industries.
Andhra Pradesh Economy and Public Finance Structure: AP Economy Structure and Growth: Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) and Sectoral Contribution, AP Per Capita Income (PCI) – AP State Income: Tax and Non-Tax Revenue – AP State Expenditure, Liabilities and Interest Payments – Central Assistance – Foreign Aid Projects – Recent AP Budget.
Agriculture, Allied Sector, Industrial Sector, Services Sector in Andhra : Production Trends of Agriculture and Allied Sectors – Cropping Policy – Rural Credit Cooperatives – Agricultural Marketing – Strategies, Schemes and Programmes related to Agriculture Sector and Allied Sectors in Andhra Pradesh including Horticulture, Animal Husbandry, Fisheries and Forestry – Construction of Growth and Industries – Recent AP Industrial Development Policy – Single Window Mechanism – Single Window Mechanism – Industrial Incentives – MSMEs – Industrial Incentives – Industrial Incentives – The structure and growth of the sector – Information Technology, Electronics and Communications in Andhra Pradesh – is the latest AP IT policy.
Section-B: Scientific Knowledge and Technology-75 marks
Technological Missions, Policies, Their Applications: National S&T Policy: Recent Science, Technology and Strategic Approaches, and National Strategies and Missions, Emerging Technology Frontiers – Space Technology: Launch Vehicles of India, Recent Indian Satellite Launches and its Applications, Indian Space Science Missions – Defence Technology: Defence Research and Development Agency (DRDO): Construction, Focus and Mission, Drdo, Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) – Information and Communication Technology (ICT): National Policy on Information Technology – Digital India Mission: Initiatives and Impact – e-Governance Programs and Services – Cyber Security Concerns – National Cyber Security Policy – Nuclear Technology: Indian Nuclear Reactors and Nuclear Power Plants – Radio Isotopes – Radio Isotopes.
Energy Management: Policy and Projections: Established Energy Efficiencies and Demand in India – National Energy Policy – National Policy on Biofuels – Bharat Stage Regulations – Renewable and Renewable Energy: Origins and Installed Capabilities in India – New initiatives in India and recent initiatives, schemes and achievements in the renewable energy sector.
Ecosystem, Biodiversity: Ecology and Ecosystem: Ecology Basic Concepts, Ecosystem: Components and Types – Biodiversity: Biodiversity: Meaning, Components, Biodiversity Hotspots, Biodiversity Loss and Biodiversity Conservation: Methods, Recent Plans, Goals, Convention and Protocols – Wildlife Conservation: CITES and Endangered Species related to India – Biodiversity Reserves in the recent past .
Waste Management, Pollution Control: Solid Waste: Solid Waste and their Classification – Disposal Practices and Solid Waste Management in India – Environmental Pollution: Types Environmental Pollution – Sources and Effects – Pollution Control, Control and Alternatives: Recent Projects, Actions and Programs to Reduce The Environment Pollution in India – Effect of Transgenics on the Environment and their Control – Eco-Friendly Technologies in Agriculture – Bioremediation: Types and Scope India.
Environment – Health: Environmental Challenges: Global Warming, Climate Change, Acid Rain, Ozone Layer Depletion, Ocean Acidification – Environmental Programs : International Events, Protocols, Conferences to Combat Recent Climate Change Special Reference to India’s Participation and Role in Combating Climate Change – Sustainable Development: Meaning, Nature, Scope, Components and Sustainable Development Goals – Health Issues: Disease Burden and Recent Trends in The Epidemic and Pandemic – Preparedness and Response: Healthcare Delivery and Outcomes in India – Recent Public Health Initiatives.

